Green Hydrogen
for industry
Green hydrogen is a key element of the energy transition and an increasingly recognized fuel of the future. It offers the potential to decarbonize sectors of the economy that are difficult to electrify, helping achieve the EU’s goal of climate neutrality by 2050.
Although the core technology for producing green hydrogen, water electrolysis powered by renewable energy, is highly mature, systemic barriers still hinder its large-scale deployment.
However, falling electrolysis costs, growing policy support, and increasing private sector interest are bringing the point of commercial viability closer than ever.
What is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced sustainably, without CO₂ emissions, most commonly through water electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources (RES). Delegated acts under the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II and RED III) define the detailed conditions under which electrolytic hydrogen can be classified as renewable (green).
The “color” of hydrogen does not describe the element itself but rather a convention indicating the production technology.


Poland is the third-largest producer of gray hydrogen in the EU, generating over 1.3 million tons annually. The challenge lies in the fact that gray hydrogen is obtained through steam methane reforming (SMR), which relies on natural gas as its primary feedstock. According to the International Energy Agency, this method emits about 9–10 kg of CO₂ for every kilogram of hydrogen produced.
This is why green hydrogen is emerging as a promising component of the ongoing energy transition.
Green Hydrogen Production Technologies
Green hydrogen is produced without greenhouse gas emissions, most commonly through water electrolysis powered by electricity. This process takes place in devices known as electrolyzers. The most widely used types include alkaline electrolyzers (ALK) and membrane electrolyzers (PEM and AEM). ALK and PEM technologies are mature and ready for large-scale commercialization, while AEM is still under development toward industrial-scale deployment.
The longest-used and still most common technology for green hydrogen production is the alkaline electrolyzer. It offers high efficiency and a long component lifespan (50,000–90,000 operating hours). In large installations, these benefits become even more significant, and the competitive cost of the equipment further strengthens investment profitability.
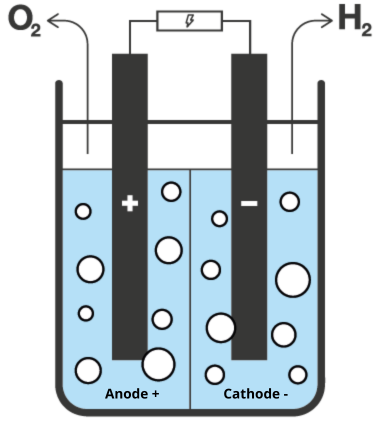

Another key requirement for green hydrogen production is renewable energy sources (RES), which must power the electrolysis process. Importantly, these capacities should be additional to existing RES to ensure that renewable energy use does not compromise decarbonization in the power sector.
Green hydrogen projects often include dedicated renewable energy facilities.
Power-to-Gas systems, which combine electrolyzers and RES, require oversizing the available renewable capacity relative to the nominal power of the electrolyzer to ensure proper operation. Variability on the RES side affects the stability of the electrolyzer and the efficiency of H₂ production.
Applications of Green Hydrogen – Hydrogen in Industry and Transportation
We are transforming the world toward green energy.
Green hydrogen is considered a key solution for decarbonizing sectors of the economy that are difficult to electrify. This is particularly relevant for industries where hydrogen already plays an essential role in industrial processes. Currently, industrial hydrogen production and on-site consumption dominate gray hydrogen output, which is why these facilities are often seen as having the greatest potential to drive a hydrogen revolution.
Refineries
Hydrogen production is essential for refining crude oil into gasoline, diesel, and other chemicals. A significant share of gray hydrogen is produced and consumed in the refining industry.

Hydrogen in transportation
Among Polish cities that have opted for hydrogen buses are Poznań, Wrocław, Wałbrzych, Konin, and Rzeszów. Hydrogen shows greater potential in long-distance, heavy-duty, and bus transportation compared to BEV (Battery Electric Vehicle) solutions, thanks to shorter refueling times and longer ranges.

Metallurgy (Steel Production)
Hydrogen plays a significant role in metallurgy, and achieving zero-emission steel production using green hydrogen is key to Europe’s climate neutrality goals. According to WiseEuropa, the steel industry alone accounts for approximately 2.5% of emissions in Poland, 5% of CO₂ emissions in the EU, and around 7–8% of global greenhouse gas emissions.

Ammonia Production
Hydrogen in the chemical industry is used as a feedstock for the production of numerous compounds, including ammonia and methanol. Ammonia production already accounts for a significant share of hydrogen demand in the EU.
Currently, the refining and chemical industries are the primary consumers of hydrogen produced in Poland. According to the Polish Economic Institute, in 2022, oil refining and ammonia production accounted for more than 96% of total hydrogen demand in the country, amounting to over 784,000 tons per year.
How Electrum Supports the Growth of Green Hydrogen
At Electrum, we are actively contributing to the hydrogen revolution by delivering the first project of its kind in northern Poland—a 5 MW electrolyzer for the Gdańsk Refinery.
The project scope includes the complete implementation of a 5 MW alkaline water electrolysis system, along with all associated infrastructure.
Electrum is responsible for the entire investment cycle: from concept design, through detailed engineering and construction design, to delivery, assembly, and commissioning of the installation.
The contract also covers civil works, foundations, sanitary and electrical installations, as well as the construction of a pipeline rack for hydrogen pipelines.

Advantages of Green Hydrogen – Why It Matters
Green hydrogen is emerging as an essential pillar for achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Beyond its critical role in decarbonizing industry—where a significant share of gray hydrogen is currently used and electrification remains challenging—and in transport, it also holds enormous potential as an energy storage medium for renewable sources.
Energy can be stored in hydrogen in chemical form and later converted back into heat or electricity. In practice, excess electricity that cannot be consumed immediately is directed to electrolyzers. The hydrogen produced can then be stored and utilized where needed, as fuel or feedstock, creating a long-term energy storage solution.
This makes green hydrogen storage a key component of the energy transition. Hydrogen also serves as a fuel for hydrogen fuel cells—electrochemical devices that convert hydrogen into electricity, playing a vital role in energy storage systems.


In integrated Power-to-Gas-to-Power systems, hydrogen produced by an electrolyzer is stored and later converted back into electricity in a fuel cell, with water as the only by-product. For efficient fuel cell operation, high fuel purity is essential. Green hydrogen from electrolysis achieves a 99.97% purity standard, enabling safe use in power systems, whereas hydrogen from reforming requires costly purification due to contaminants that could poison the fuel cell.
Its greatest advantage is zero CO₂ emissions during production, provided the electricity for electrolysis comes from renewable sources. Green hydrogen thus supports global climate goals and helps build new pillars of energy security.
Electrum – Your Partner in Hydrogen Projects
With nearly 30 years of experience in the energy sector and a strong engineering background, Electrum provides comprehensive support for hydrogen projects
- from analysis and concept development,
- through design and construction,
- to integration with energy management systems and operational support.
We combine expertise in CAPEX and OPEX optimization with in-depth knowledge of the market and EU regulations. Our mission is to transform ambitious visions into fully operational installations.
Green Hydrogen in Poland
The Polish Hydrogen Strategy until 2030 with a Perspective to 2040 (PSW), published in October 2021, is a strategic document defining the main objectives for developing Poland’s hydrogen economy.
The overarching goal of the PSW is to establish and grow the Polish hydrogen industry to support climate neutrality and maintain the competitiveness of the national economy. Hydrogen is intended to serve as an energy storage medium, accelerating progress toward decarbonization.
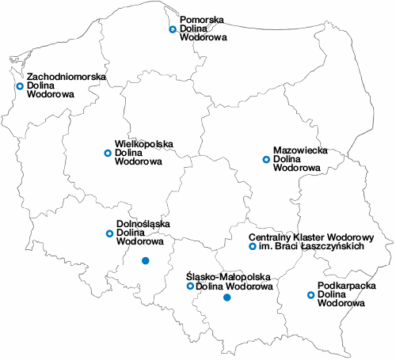

The PSW aligns with European Union initiatives such as the EU Hydrogen Strategy and the European Green Deal, and is consistent with the framework of the Paris Agreement.
In mid-2024, the “Hydrogenization of the Economy” program was launched with a budget of PLN 1.1 billion under the National Recovery Plan (KPO). Additional funding programs are also available, including those from the National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management (NFOŚiGW), such as “Support for Electric Vehicle Charging and Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure.
Operational scheme of a 5 MW electrolyzer for the Gdańsk Refinery

Your Hydrogen Project Starts Now
The potential of green hydrogen is enormous. It is no longer a technology of the future—it is rapidly becoming a technology of today. The tipping point for its widespread adoption is approaching faster than anyone anticipated.
At Electrum, we are ready to help your organization enter the era of green hydrogen—from the initial concept to a fully operational installation.
