In this article, we present the key steps how to start a solar farm. Building a solar photovoltaic power plant is certainly not easy. Most stages require the help of specialists, but before reaching out for their assistance, it is worth understanding the process of constructing a solar farm.
The stages of establishing a solar farm can be divided into design stages (site selection, administrative procedures, construction design) and execution stages (solar farm and accompanying infrastructure construction, electrical connections and testing). Following these stages, there are also aspects related to the effective management of the installation, which will impact the future of the farm.
Quick Facts:
- The installed capacity of photovoltaics in Poland at the end of February 2025 amounted to 21.8 GW.
- In 2023, solar installations accounted for about 60% of the installed capacity in the entire renewable energy sector, according to the latest report from the Institute of Renewable Energy. This means that photovoltaics lead the way in the renewable energy sector.
- By the end of 2023, Poland’s photovoltaic capacity reached 17.08 GW, saving around 23 million tons of CO2 emissions, according to the IEO report.
- Based on photovoltaic installation capacity, we distinguish between small and large farms. A small farm is an installation with a capacity ranging from 50 kWp to 1 MW. A large photovoltaic installation has a capacity above 1 MW.
- A photovoltaic power plant is an installation with a capacity of 1 MW or more.
- To install a 1 MW photovoltaic power plant, approximately 2 hectares of land are required.

How to start a solar farm? Design Stages of Creating a solar power plant
1. Choosing the Location: Finding the Right Land for Photovoltaics
Where to begin? The most important step is choosing the location for the photovoltaic farm, which must take into account many factors such as land suitability for the investment, sunlight availability, and proximity to the grid infrastructure. A suitable location for a photovoltaic farm is one that primarily:
- Utilizes land with low agricultural value (requirements for solar farms include land of class IV or lower), which does not block areas capable of food production, simplifies administrative procedures, and also reduces the investment cost.
- Is well-sunlit, where sunlight availability is the measure of the amount of solar energy reaching the Earth’s surface within a specified time, expressed in kilowatt-hours per square meter (kWh/m²) per day. Determining sunlight availability allows for a preliminary assessment of how much solar energy can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic panels, and thus a preliminary assessment of the photovoltaic farm’s profitability.
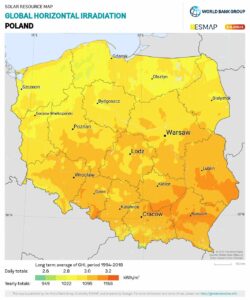
- It allows for the proper placement of PV panels, which is best ensured by flat terrain; however, it is possible to optimally utilize land with a slight slope towards the south.
- Proximity to grid infrastructure is another important factor, which means more favorable conditions for connecting the photovoltaic farm to the power grid. This directly impacts the construction costs and profitability of the photovoltaic farm. Locating the farm near existing transmission lines and transformer stations simplifies the procedures, so the recommended distance of the investment from the power grid is a maximum of 200 meters. Specific requirements for this distance may vary depending on local regulations and technical possibilities.
- It is located at an appropriate distance from residential buildings or public utility areas. It is generally accepted that the minimum distance from buildings is about 100 meters, which minimizes potential nuisances related to noise and light reflections. Actual requirements may depend on local regulations and the specifics of the project.
Learn more about the locational conditions for building a photovoltaic farm: How to Choose the Best Location for Solar Panels
2. Project Procedures: Required Permits and Legal Regulations
If you have a plot of land that meets the initial criteria for establishing a photovoltaic farm, it is important to verify whether a solar farm can be built on that area. This involves considering legal regulations, such as environmental conditions, the local zoning plan, or other administrative decisions for the land.
Local Zoning Plan
If a local zoning plan exists for the area, you must check whether it allows the construction of a photovoltaic farm. If the LZP permits the construction of solar farms, the investor must comply with all the conditions outlined in the plan. If the LZP does not allow for the construction of such farms, an application must be submitted to amend the plan, which can be a lengthy and tedious process. In the absence of an LZP, it is necessary to apply for a decision on building conditions.
Environmental Decision
Obtaining permits also involves securing an Environmental Decision (ED). This is required when the area covered by the outer edges of the panels exceeds 0.5 hectares in protected areas or 2 hectares in other areas. The requirements for obtaining an ED include conducting an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), which involves preparing an environmental report, holding public consultations, and obtaining opinions from various institutions. The decision is issued by the mayor, town mayor, or city president.
Building Permit
After obtaining the ED and meeting the requirements of the LZP, it is necessary to secure a building permit. This process includes preparing a detailed construction design and submitting an application to the appropriate architectural and construction administration authority. The building permit specifies the detailed building conditions for the photovoltaic farm, including the technical and legal requirements that the investment must meet.
Connection to the Power Grid
Required permits also include a document issued by the Distribution System Operator (DSO) or Transmission System Operator (TSO) that outlines the technical requirements for connecting the installation to the National Power System (NPS). This process involves a technical analysis, potential connection fees, and compliance with specified technical standards.
Read more:
How to Effectively Obtain Connection Conditions for a PV Farm?
License
For commercial photovoltaic farms and those with a capacity exceeding 1 MW, a license for the production and further sale of energy from the photovoltaic farm is required. Obtaining a license involves submitting an application to the Energy Regulatory Office (ERO). This process includes presenting a detailed construction project of the photovoltaic farm, technical documentation, and obtaining the previously mentioned administrative and environmental permits. The license is essential for the legal operation of the farm and the sale of energy from the photovoltaic farm to the power grid.
Solar Farm Construction Project: Formalities Before Construction
Before obtaining a building permit, it is necessary to prepare a photovoltaic installation project, which involves creating detailed technical documentation, including the site development plan, architectural and construction design, and technical design.
Site Development Plan
The first step is to create a site development plan, which includes the layout of photovoltaic panels, access roads, technical infrastructure, and other elements necessary for the operation of the solar farm. This plan must take into account the topography of the land, its sunlight exposure, and the existing infrastructure.
Architectural and Construction Design
The next component is the architectural and construction design, which includes detailed technical solutions for the supporting structures of the panels, foundations, fences, and other construction elements. This design must comply with all building codes and technical requirements.
Technical Design
Simultaneously, a technical design is developed, which contains detailed information on the electrical installation, monitoring systems, fire protection, and other technical systems necessary for the safe and efficient operation of the photovoltaic farm. This design also includes the technical specifications of the equipment used and the materials from which various installation elements will be made.
Read more:
Solar Farm Design – What You Need to Know?
Finding the right location, dealing with all the necessary administrative and legal steps, and creating various designs – the design process of setting up a photovoltaic farm is demanding. A sensible solution is to seek the help of specialists. At Electrum, we manage investment projects from concept to managing energy production from the photovoltaic farm.
How to Start a Solar Farm? Execution Stages of Creating a PV Farm
Once the building permit is obtained, the construction of the photovoltaic farm can begin, which involves several key stages. How do you start the construction?
1. Preparing the Site for Construction
The first step in building a photovoltaic farm is preparing the site for the installation of PV panels. This process includes removing any obstacles, leveling the ground, and preparing the foundations that will ensure the stability of the entire structure. The foundations must be properly designed and constructed to meet the requirements of the photovoltaic farm construction.

2. Installation of PV Panels
The next stage is the installation of the panels. The panels are mounted on the prepared foundations in a layout that maximizes the use of available sunlight. The construction of a photovoltaic panel farm must be precise to ensure the efficiency and durability of the solar power plant. The installation also includes setting up the supporting structures and systems to protect against various weather conditions.
3. Electrical Connections and Testing
After the panels are installed, the next step involves electrical connections and testing, which are crucial to confirm that the entire system is functioning correctly, meeting energy safety requirements, and complying with technical standards. The procedures related to electrical testing include verifying connections and checking the performance of the modules.
Once everything is ready, a visit to the Distribution System Operator is necessary to finalize the agreement and conduct the final inspection.
Read more in our guide: Solar farm construction: A Comprehensive Guide
How Long Does It Take to Build a Solar Farm?
The execution phase of the investment takes relatively little time. For a 1 MW farm, this stage typically takes about 2-3 months. The most time-consuming part is the design phase, with a strong focus on obtaining approvals and administrative decisions. The entire process (both phases) can take up to 2.5-3 years.

Costs of Building a Photovoltaic Farm and Financing the Investment
The cost of constructing a 1 MW solar farm depends on many factors. Estimates vary based on variables such as natural conditions, project support costs, material prices, construction costs, and the price of systems and technologies used to manage the farm. The cost of such a farm can range between 2,000,000 and 4,000,000 PLN (440,000 to 920,000 EUR.)
If sufficient capital is not available, there are several ways to finance the construction of a photovoltaic farm. Besides loans, one option for securing funds is to take advantage of photovoltaic subsidies. The development of renewable energy in Poland and the growth of photovoltaic farms has led to increased opportunities in this area. Available options include, among others, EU Funds for 2021-2027, as well as regional programs.
How much to start a solar farm?
The profitability of a photovoltaic farm depends on many factors, including total construction costs, financing methods, production efficiency, and energy sales conditions, making it unique to each project.
To illustrate the earnings from a farm, we can use a simplified calculation. Assuming annual production of 1,100 MWh and a price of 600 PLN per MWh, the annual revenue can be calculated as follows:
1,100 MWh/year * 600 PLN/MWh = 660,000 PLN/year After 8 years, the total revenue would be: 5,280,000 PLN (1,160,000 to 1,210,000 EUR).
A photovoltaic investment can be very beneficial, especially in the context of growing demand for renewable energy and the availability of various forms of funding. After a few years, which yield a return on investment, the farm enters a period of steady and stable income, which is the profit from the farm.
Different types of solar power plants generate different revenues. Depending on the purpose of the farm’s construction and the business model, the energy produced by the photovoltaic farm may be intended for self-consumption or for sale.
Monitoring and Management
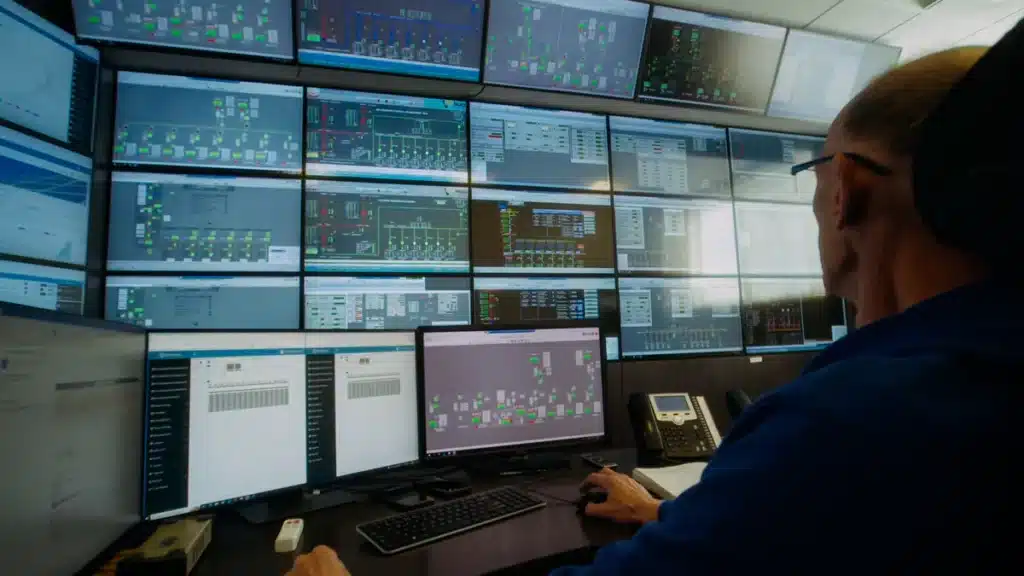

Professional management of a photovoltaic farm through effective monitoring ensures the maximization of profits, extension of the power plant’s lifespan, and helps reduce maintenance costs by enabling quick responses to potential issues.
Read more about solar farm monitoring methods at Electrum:
SCADA System on a Large-Scale PV Farm | Electrum Case Study
Now you know how to start a solar farm, and if you have any questions, feel free to contact us!






