Progressive climate change represents one of the greatest challenges facing the modern world. Actions supporting the reduction of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere play a crucial role in preventing it. This particularly applies to the industrial sector, whose development model has largely been based on fossil fuels until now. Changes in this area, concerning the need to minimize emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere, are generally referred to as industrial decarbonization. What exactly does this process entail? You’ll find the answer to this question in today’s article.
Industrial Decarbonization – What Does It Mean and Why Is It Crucial?
Economic decarbonization is the systematic reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other harmful greenhouse gas emissions through the implementation of appropriate technological, energy-related, and organizational changes in enterprises. It does not solely involve replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources (RES), but also encompasses the modernization of production processes, implementation of closed-loop material flows, and the application of innovative solutions that minimize negative environmental impact without the need to sacrifice high efficiency.
This is important primarily due to the need to protect the climate and the planet’s resources. As indicated by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere reached a record value in 2024 – 423.9 parts per million. An appropriate response from the industrial sector to this problem can translate into an effective fight against global warming.
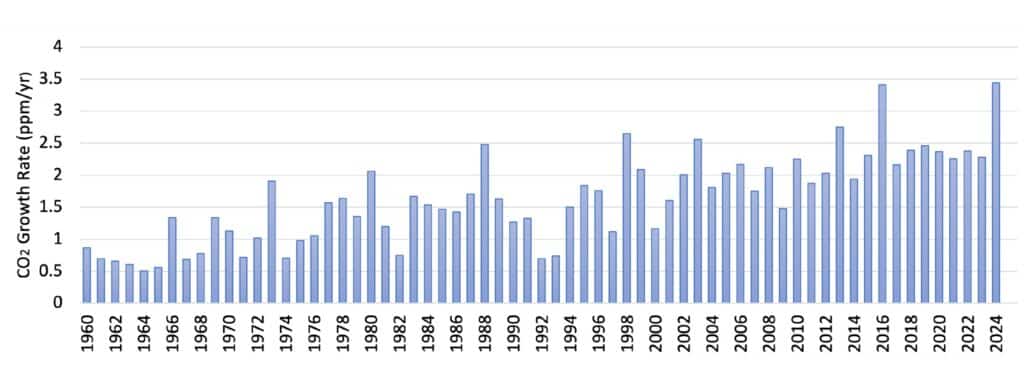
Source: WMO Greenhouse GAS Bulletin No.21
What Are the Main Principles of Industrial Decarbonization?
This process is based on several priority actions, such as:
- Moving away from fossil fuels – this is the most important goal, involving the replacement of hard coal, lignite, or crude oil with clean energy from renewable sources (see: Industrial solar power: What You Need to Know and How to Get Started);
- Increasing energy efficiency – reducing energy demand through the implementation of systems that optimize its consumption and modernization of production processes;
- Limiting emissions resulting directly from technological processes – this involves the application of solutions such as green hydrogen;
- Introducing a circular economy – this helps reduce the consumption of primary raw materials while minimizing the amount of waste generated.
- Digitalization of industry – advanced automation solutions allow for precise monitoring of energy consumption and emission levels at every stage of production; they also enable process optimization and decision-making appropriate to specific needs.
All these actions are based on implementing solutions that do not negatively affect enterprise efficiency, thus not halting industrial development.
What Results Does Industrial Decarbonization Bring?
Industrial decarbonization translates into numerous benefits for both the natural environment and enterprises that decide to operate in accordance with its principles. Environmental benefits include:
- Effective prevention of climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improvement of air quality, especially in heavily industrialized areas, which also translates into a healthier society;
- Reduced utilization of natural resources thanks to recycling and the circular economy.
- Protection of ecosystems by limiting environmental degradation resulting from resource exploitation;
- Preservation of the planet’s potential for future generations.
Companies that contribute to industrial decarbonization can also count on a number of benefits. Above all, investing in solutions that improve energy efficiency allows them to reduce operational costs while improving business resilience to energy crises. It also influences the competitiveness of a given company – growing environmental awareness among consumers means that the market increasingly rewards climate-friendly products.
What Technological Innovations Support Emission Reduction in Industry?
As mentioned, modern technologies constitute an important element of the economic decarbonization process. In addition to RES installations such as wind and solar power plants, solutions worth highlighting include:
- Green hydrogen – produced through water electrolysis using renewable sources- finds application in transportation, the chemical industry, and also serves as a stabilizer for energy grids.
- Intelligent control systems – the use of the Internet of Things (IoT), data analysis, and automation to minimize energy and raw material losses and increase efficiency;
- Energy storage – allows for efficient use of renewable energy, enabling industrial processes to operate even with variable RES production.
- Circular economy and recycling – recovery of materials and their reintroduction into production.
Thanks to these solutions, the industry can not only limit its impact on the climate but also increase efficiency, save raw materials, and prepare for growing regulatory requirements and market expectations.
Also read: Cable Pooling – Optimal Resource Utilization and RES Development.
Which Industrial Sectors Require Decarbonization?
When discussing industrial decarbonization, particular attention is paid to sectors responsible for the largest greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. This concerns, for example, metal production, which involves generating large amounts of CO₂. According to the Net-Zero Industry Tracker 2024 report, the most problematic areas in this regard are sectors such as steel, cement, aluminum, and chemical production, which together account for a significant portion of emissions.
Transportation also requires decarbonization – not only road transport but also industrial transport, covering the movement of raw materials and products in large quantities. Electrification of corporate transport fleets would allow for a reduction in air pollutants.
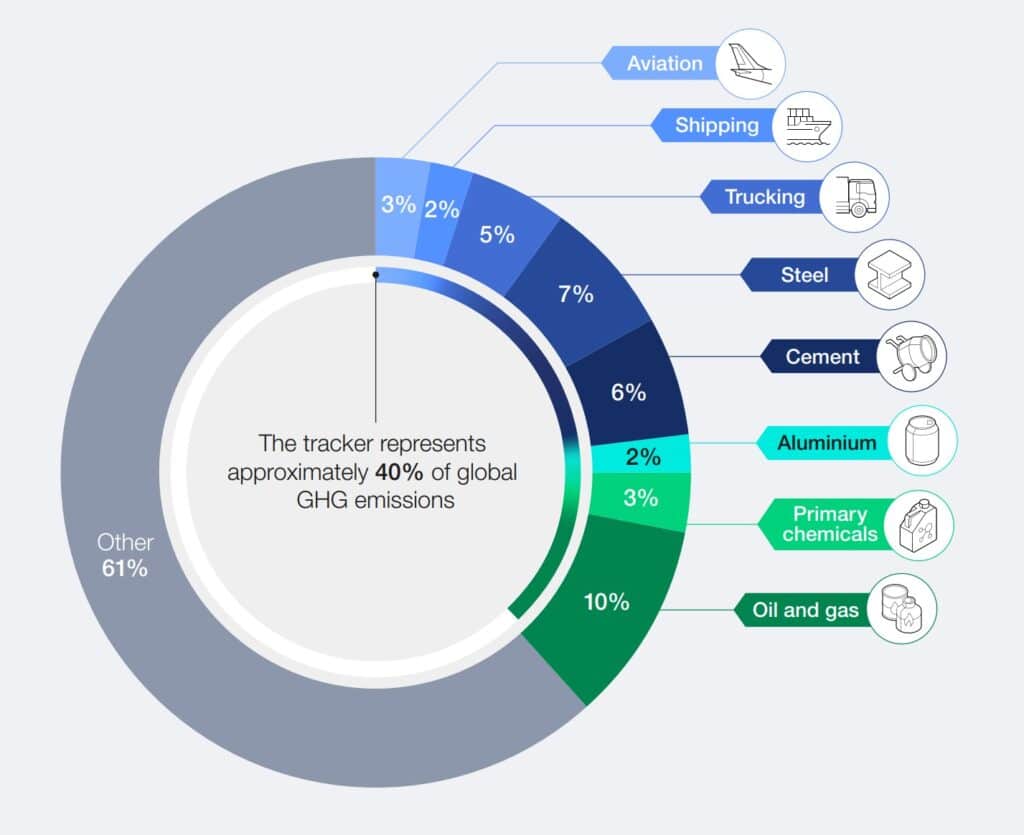
Source: World Economic Forum, Net-Zero Industry Tracker 2024
Industrial Decarbonization in Poland – What Challenges and Opportunities Do We Face?
Polish industry is highly energy-intensive and still largely relies on fossil fuels, which causes high CO₂ emissions. Steel, cement, chemical, and aluminum producers, as well as the petrochemical industry, are among the main greenhouse gas emitters in our country. The most important challenges in the process of industrial decarbonization in Poland include:
- High transformation costs – modernization of industrial plants and introduction of new technologies require enormous financial outlays. In many cases, these costs are a barrier to the rapid implementation of low-emission solutions.
- Dependence on coal and gas – Poland still largely uses hard coal and lignite in energy production and industry.
- The need to adapt industry to European Union (EU) requirements – this involves the necessity of reporting emissions and implementing reduction plans. Failure to adapt may result in additional costs and loss of competitiveness in the European market.
- Industrial decarbonization requires new competencies – specialists in RES, hydrogen technologies, energy efficiency, or process digitalization.
However, this is not a hopeless situation – Poland has the opportunity to significantly reduce industrial emissions through investments in modern technologies in heavy sectors such as steel, cement, or chemical production. The development of renewable energy sources and green hydrogen allows for independence from fossil fuels, while digitalization and automation of production processes increase energy efficiency and reduce raw material consumption. Access to EU funds, meanwhile, helps to implement this process more quickly.
How Does Electrum Support Industrial Decarbonization?
At Electrum, we actively work toward energy transformation in Poland, implementing large-scale RES projects for years. We work comprehensively, providing both investment planning and general contracting, as well as long-term management of installations.
We implement photovoltaic and wind projects, as well as hybrid power plants combining various energy sources. Additionally, we use advanced monitoring and energy asset management systems, which improve installation efficiency, reduce energy losses, and increase the profitability of implemented technologies. We are also involved in the development of hydrogen projects – thus effectively supporting industrial decarbonization in Poland and foreign markets.
We believe that intensive actions toward energy transformation will allow us and future generations to live in a world where zero emissions become the standard.



